3 page website examples services
A website is a collection of web pages and related content that is identified by a common domain name and published on at least one web server. A website may be accessible via a public Internet Protocol (IP) network, such as the Internet, or a private local area network (LAN), by referencing a uniform resource locator (URL) that identifies the site. Websites can have many functions and can be used in various fashions; a website can be a personal website, a corporate website for a company, a government website, an organization website, etc. Websites are typically dedicated to a particular topic or purpose, ranging from entertainment and social networking to providing news and education. All publicly accessible websites collectively constitute the World Wide Web, while private websites, such as a company's website for its employees, are typically part of an intranet. Web pages, which are the building blocks of websites, are documents, typically composed in plain text interspersed with formatting instructions of Hypertext Markup Language (HTML, XHTML). They may incorporate elements from other websites with suitable markup anchors. Web pages are accessed and transported with the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which may optionally employ encryption (HTTP Secure, HTTPS) to provide security and privacy for the user. The user's application, often a web browser, renders the page content according to its HTML markup instructions onto a display terminal. Hyperlinking between web pages conveys to the reader the site structure and guides the navigation of the site, which often starts with a home page containing a directory of the site web content. Some websites require user registration or subscription to access content. Examples of subscription websites include many business sites, news websites, academic journal websites, gaming websites, file-sharing websites, message boards, web-based email, social networking websites, websites providing real-time stock market data, as well as sites providing various other services. End users can access websites on a range of devices, including desktop and laptop computers, tablet computers, smartphones and smart TVs. The World Wide Web was created in 1990 by the British CERN physicist Tim Berners-Lee.[1] On 30 April 1993, CERN announced that the World Wide Web would be free to anyone with a computer and a modem connection.[2] Before the introduction of HTML and HTTP, other protocols such as File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and the gopher protocol were used to retrieve individual files from
There are many different types of websites that offer services. Some examples of these types of websites are e-commerce websites, service websites, and subscription websites. Each type of website offers different services and features. E-commerce websites allow users to purchase products and services online. Service websites provide users with a way to find and book services online. Subscription websites offer users access to content that is only available to subscribers.
After looking at these three examples of effective websites for service-based businesses, it's clear that there are some key elements that all effective websites for service-based businesses share. First, all of these websites have a clear and concise message about what the business does and what services they offer. Second, each website makes it easy for visitors to contact the business and learn more about their services. Finally, all of these websites have a professional design that instills confidence in the business and its services. By keeping these elements in mind, you can create an effective website for your service-based business that will help you attract new clients and grow your business.
Top services about 3 page website examples

I will design a slick wordpress site with divi
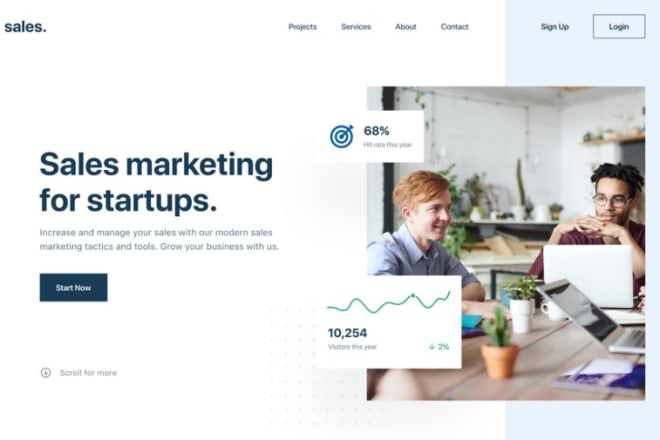
I will create custom portfolio or landing page website for your business

I will design minimalist landing page website with squarespace
I will make a landing page or a website design in 24 hours

I will design modern and unique landing pages
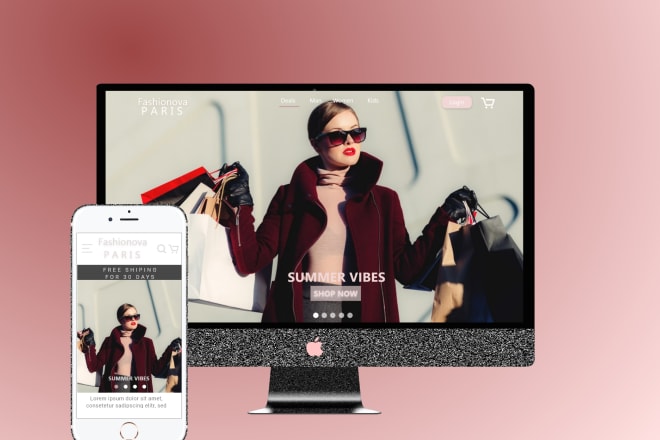
I will design creative one page or landing page website UI UX

I will create landing page website using wordpress and elementor

I will create attractive landing page, web page, website

I will write your website contents or squeeze page or homepage contents
These are some of the reasons why you should hire a professional:
- A good website content will increase sales
- Makes your website professional
- A great About Us page will definitely help increase sales.
- I can also write other pages for your website; message me for that extra service.
Your About Us page will be written by me, a native English speaker and will be grammatically correct. If you need anything additional, feel free to contact me for details.
I also have several examples I can show you. I have written several contents for top websites like HuffPost, healthable, Wikeria and many others.
ORDER NOW!
If you need additional services like
I can help you with:
- Homepage
- Services Page
- About us/Who we are Page
- Contact Us
- Terms and Condition
- Privacy Policy
- FAQ's
- Any Page OF YOUR CHOICE
Contact me and let us discuss it.

I will design modern, price list, pricing table etc
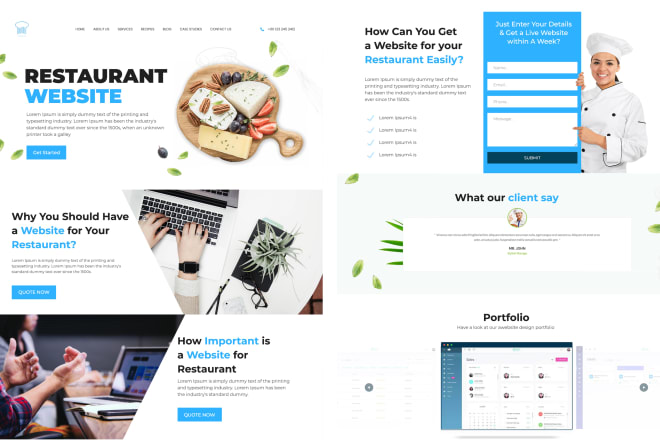
I will design website template in PSD or xd
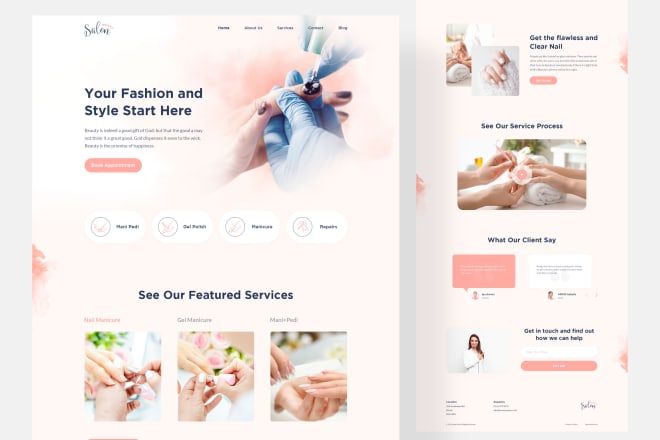
I will design the ui ux of your website and landing page

I will do on page and off page SEO of your website
- Website Audit
- Content optimization
- Keyword research
- On page SEO
- Off page SEO
- Measurement
With 5 years of experience doing local and international SEO, I can ensure quality service to bring your website on 1st page of Google within 1-3 months.
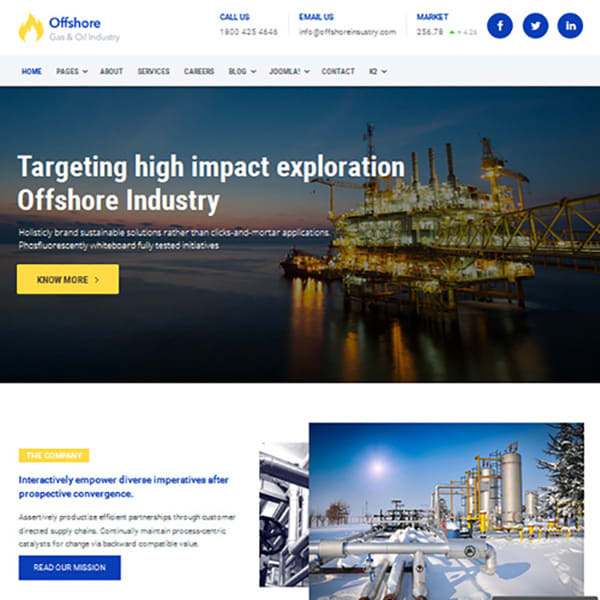
I will do website design and SEO
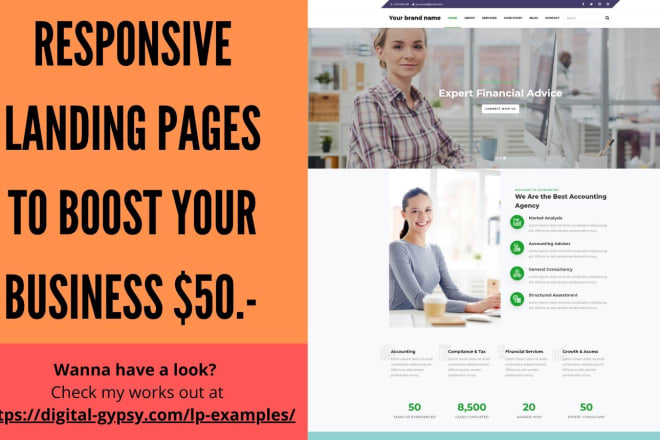
I will craft a professional landing page for your business
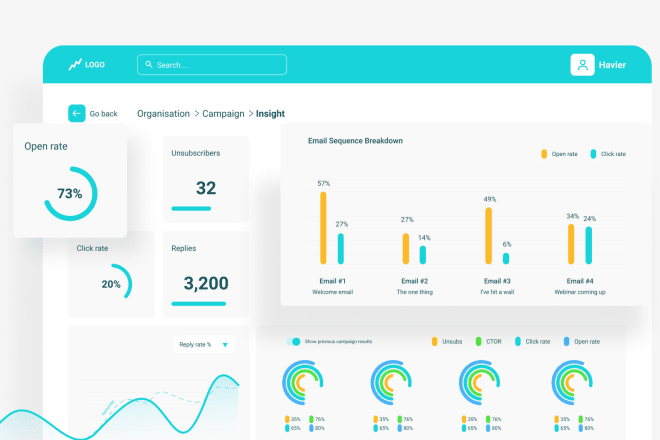
I will design a professional and modern website UI design for you
I will design web template in PSD, xd or figma website
