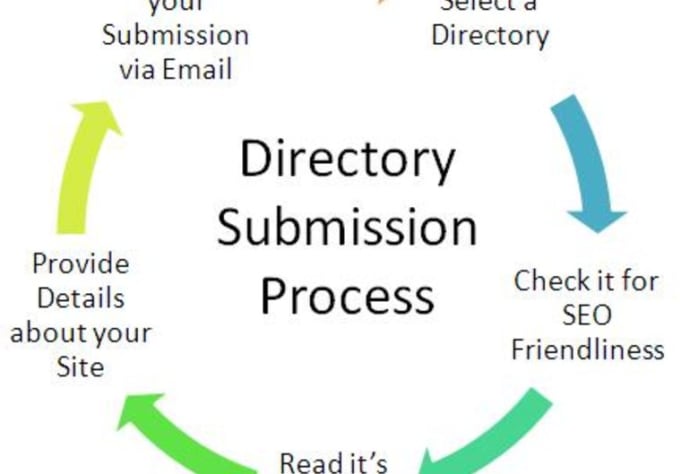
Active directory lightweight directory services wiki
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), formerly known as Active Directory Application Mode (ADAM), is a directory service that runs as a stand-alone application. Unlike Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), which stores data in the form of a hierarchical namespace, AD LDS uses a flat namespace. AD LDS is designed to provide directory services for applications that use LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), such as Microsoft Exchange Server and Microsoft Internet Authentication Service (IAS).
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) is a directory service that provides a flexible approach to directory storage and management for application developers. AD LDS runs as a service on Windows Server operating systems. It stores data in an extensible schema, which can be customized to meet the directory needs of the application. AD LDS provides the same core directory services features as Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), such as security and authentication, but it does not require the deployment of domains or domain controllers.
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) provides a flexible means of storing and replicating directory data for applications, services, and users that requires directory data outside of the domain namespace. AD LDS runs as a service on Windows Server operating systems. Because AD LDS uses the same code base as Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), it is sometimes referred to as Active Directory Application Mode (ADAM).
Top services about Active directory lightweight directory services wiki
I will develop lms learnpress membership, online course website

I will design and develop your professional website with wordpress and elementor
I will design interactive wordpress website to grow your business

I will develop a directory listing website with mylisting theme

I will create a directory website for you

I will do complete seo of your site for 1st page ranking on google

I will wordpress directory website using mylisting theme
I will create directory listing business wordpress website business
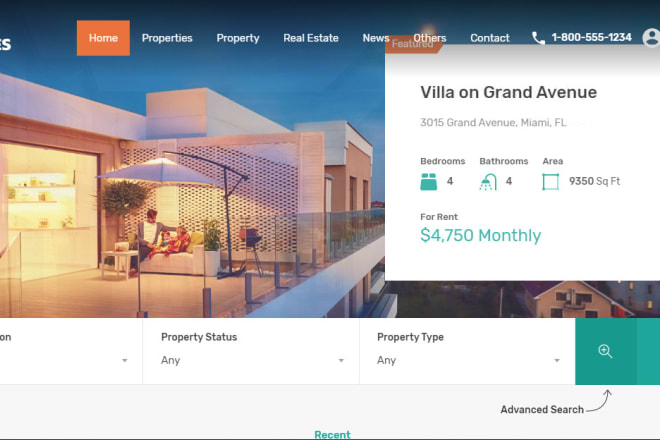
I will do real estate listing directory site mylisting listingpro
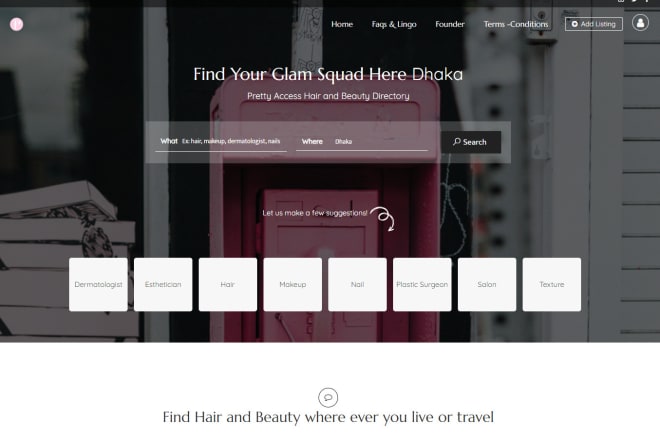
I will build wordpress listing directory and classified site
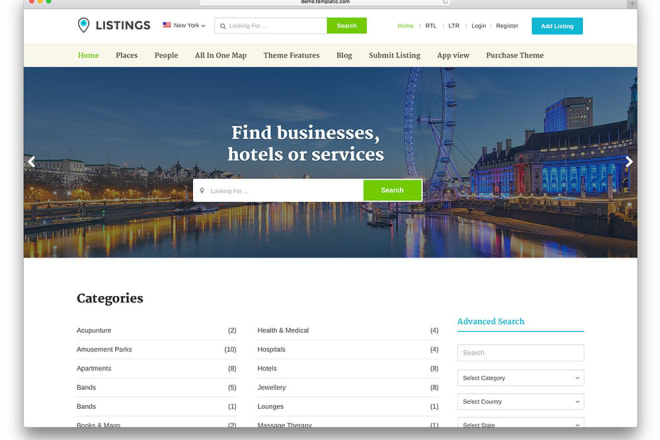
I will create wordpress directory listing business website
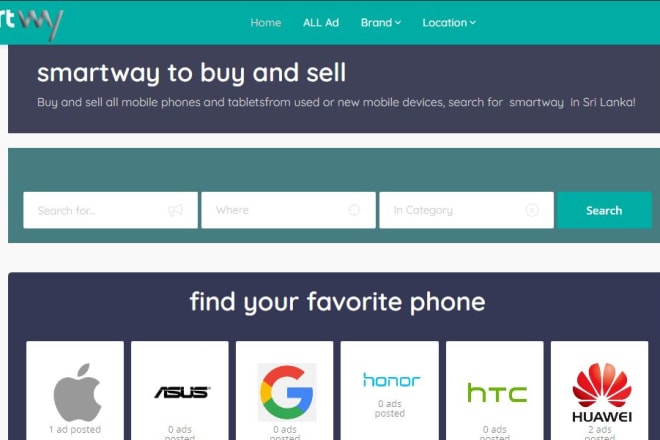
I will build classified web site for specific category or all

I will do 30 high pr USA web directory submissions

I will do 30 high pr USA web directory submissions

I will create 1500 USA directory submission links
I will design wordpress directory website using listing pro,mylisting