Develop for android services
Android is a mobile operating system developed by Google, based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open source software and designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android's user interface is mainly based on direct manipulation, using touch gestures that loosely correspond to real-world actions, such as swiping, tapping and pinching, to manipulate on-screen objects, along with a virtual keyboard for text input. In addition to touchscreen devices, Google has further developed Android TV for televisions, Android Auto for cars, and Wear OS for wrist watches, each with a specialized user interface. Variants of Android are also used on game consoles, digital cameras, PCs and other electronics. Developed by Android Inc., which Google bought in 2005, Android was unveiled in 2007, with the first commercial Android device launched in September 2008. The operating system has since gone through multiple major releases, with the current version being 9.0 "Pie", released in August 2018. Android is also associated with a suite of proprietary software developed by Google, called Google Mobile Services (GMS) that frequently comes pre-installed on devices.
There is a lot to learn about developing for Android services. However, some key things to keep in mind are that Android services are very versatile and can be used to perform a variety of tasks. They are also very resource-intensive, so it is important to be mindful of how they are used.
Android services are a great way to develop for the Android platform. They allow you to develop for a wide range of devices and provide a great user experience.
Top services about Develop for android
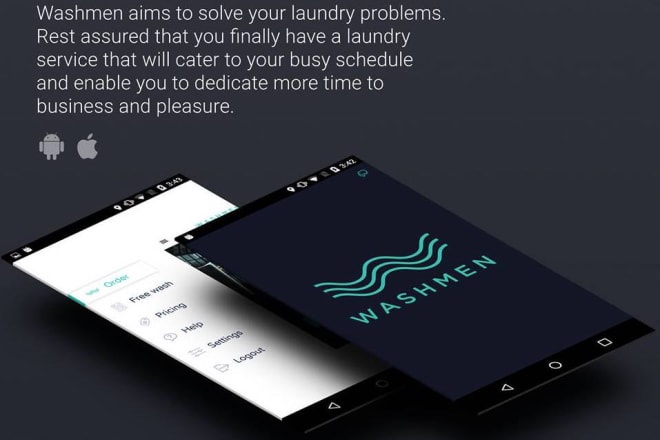
I will develop the android app in kotlin or android app developer

I will develop an android app and be your android app developer
I will develop an android app or will be your android app developer
I will develop an android app or will be your android app developer

I will develop your android apps or be your android developer

I will develop android applications for you
Over the years, I believe that following are the types of projects i am best at regardless the fact that i can develop any type of application.
- Android app development
- Android game development(Quiz base)
- Android Stealth Application
- Android App Upgrading and Modification
- Android Crashing Problem
I will develop an android app in android studio
I will develop custom android application
Android is a free OS and there are thousand of the users around the world. if you want to expand your business and want to develop a custom android application,or you want to have android application for your website, or you want to earn with android application i can help you develop android application and help you till you upload it to play store.
Notes:
- For integration with website you must have API, in case you don't have API you have to bear API Cost too.
- To publish android application on Play Store you need google play account and you have to pay $25 for the account creation so you must create google play account by your own i will help you publishing app on google play
- Basic Application consist only single Activity Application with static content

I will develop android app with php web services and sql database

I will develop an android app from scratch
I have 5+years of experience in developing android apps using android studio.
With the Past Experience of more than 30+ Android Apps i can deliver you the exact thing which you actually desire.
IDE used :- Android Studio
Language - Java
I will develop custom android app
I will develop complete android app with source code
I will develop your Android App with Splash Screen(if you want) VERY fastly, uniquely, attractively with wow factor. You will find it hot.
So, if you want to have done your App as soon as possible, then contact me.
You will pleased by my work.

I will develop android application for you
i have also work on android studio on last 6 months.
i have develop android application in android studio and android eclipse both the platform.
please read this.
1. i have charge base on application.
2. i have put various types of animation like menu drawer,Screen animation,button animation.
3. i have also develop material design base application.
I will develop best android applications with google firebase
