Ghost paywall services
As digital media consumption has increased, so has the use of paywalls by news organizations. A paywall is a system that requires users to pay for access to content. The New York Times was one of the first major news organizations to implement a paywall in 2011, and since then, many others have followed suit. There are a few different types of paywalls, but the most common is the metered paywall. This type of paywall allows users to access a certain number of articles for free before they are asked to pay. The New York Times uses a metered paywall, and it has been successful in increasing revenue. Other news organizations, such as The Wall Street Journal and The Washington Post, have implemented more strict paywalls, known as hard paywalls. These paywalls do not allow users to access any content without a subscription. There are also ghost paywalls, which are a type of soft paywall. Ghost paywalls allow users to access some content without a subscription, but they limit the amount of content that can be accessed. For example, a user might be able to read three articles per month for free, but after that, they would need to subscribe to read more. The use of paywalls has been controversial. Some people argue that paywalls are necessary to support quality journalism, while others argue that they are a barrier to access. However, there is no doubt that paywalls have become an important part of the digital media landscape.
There are a few different types of ghost paywall services, but they all basically work by allowing you to access content that is normally behind a paywall without actually paying for it. This can be done by using a proxy server or by simply bypassing the paywall altogether.
Overall, it seems that ghost paywall services are a great way to get around the paywalls of certain websites. They are easy to use and can be quite effective. However, it is important to remember that these services are not perfect and can sometimes fail to work as intended.
Top services about Ghost paywall

I will ship a newsletter and blog site that can be hosted for free

I will ship a ghost blog site that can be hosted for free
I will create, customize, design ghost themes for you

I will create responsive ghost theme
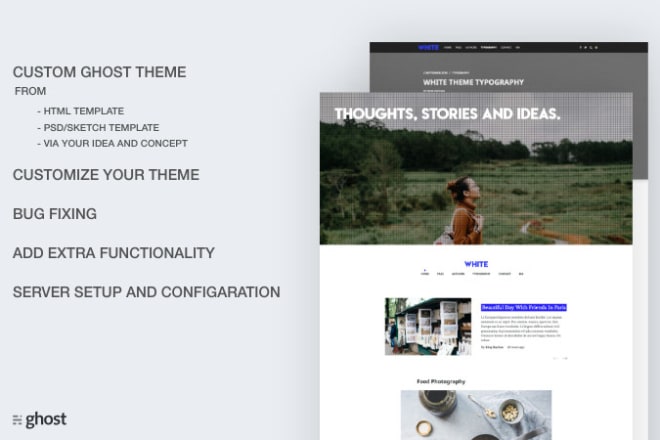
I will create a custom ghost theme

I will customize ghost theme as per your requirement
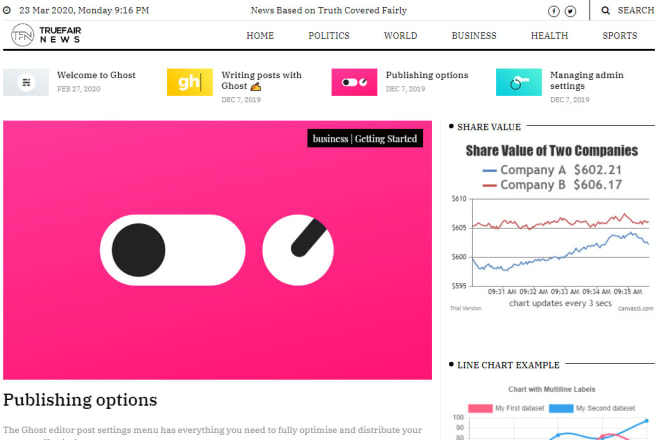
I will install and setup ghost cms

I will setup and install ghost cms for your blog and website

I will install, configure ghost blog for you

I will creating a ghost mannequin, 3d mannequin effectmannequin

I will be your secret ghost producer
I've been producing EDM, hip-hop & pop music for 7+ years and have been ghost-producing for 3+ years. My music has been featured on Spinnin Records', Armada Records, Revelead Recordings, Dim Mak & many more. My ghost-produced track has been played at major events and huge clubs around the world by big-name DJ's.
