Php parse json data services
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format. It is easy for humans to read and write. It is easy for machines to parse and generate. It is based on a subset of the JavaScript Programming Language, Standard ECMA-262 3rd Edition - December 1999. JSON is a text format that is completely language independent but uses conventions that are familiar to programmers of the C-family of languages (C, C++, JavaScript, etc). These properties make JSON an ideal data-interchange language. JSON has two primary parts: 1. A collection of name/value pairs. In various languages, this is realized as an object, record, struct, dictionary, hash table, keyed list, or associative array. 2. An ordered list of values. In most languages, this is realized as an array, vector, list, or sequence. These are universal data structures. Virtually all modern programming languages support them in one form or another. It makes sense that a data format that is interchangeable with programming languages also be based on these structures.
There are a few different ways to parse JSON data in PHP. The most popular methods are to use the built-in functions json_decode() and json_encode(), or to use the third-party library JsonSerializable.
Overall, PHP has many built-in functions that allow developers to work with JSON data. In addition, there are many third-party libraries that can be used to parse and manipulate JSON data. With so many options available, there is no excuse not to be able to work with JSON data in PHP.
Top services about Php parse json data

I will integrate API into your any web application

I will create bash shell,perl or python script

I will write an php script to parse json file
I will do web scraping, data mining, utilize soap, rest api to parse xml json rss feed

I will scrap any website you provide and do excel data processing

I will parse json data in php

I will parse json, rest api data using PHP

I will parse json and XML in php, java, javascript
I will do XML parsing to CSV file, json parsing, convert CSV to XML
I will parse json or xml into csv or excel
I will parse your json data in to android application
Hello!
Expert in JSON parsing using Retrofit ,Volley, In Android or IOS App
Sometimes you want to integrate 3rd party API in your website but don't know how to parse JSON, I can do it for you!
So please feel free to ask any question you have and let's get the work done!
Thanks!
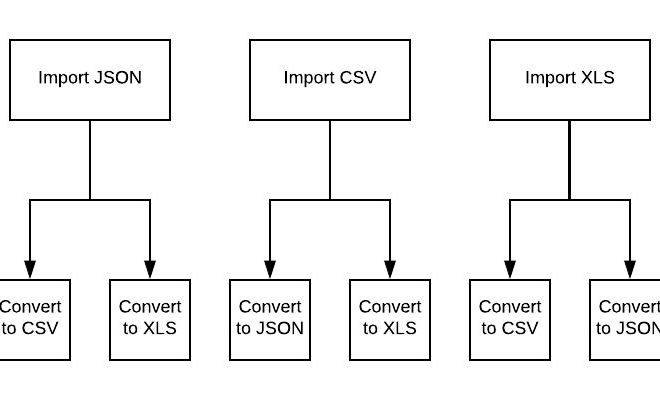
I will do convert json xml csv and excel into any specific format

I will do json and XML

I will be your jQuery assistant
I can help you in the following js skills
- AJAX
- JSON parse
- XML parse
- HTML parse
- External JS libraries
Explain your idea I can make a simpler flow for you at the earliest possible time.
Check out my other Gigs also for Combining and Make some endless possibilities of ideas that you can Convert and Make use of it.