Web architecture wikipedia services
In the early days of the World Wide Web, there were only a few simple ways to share information between computers. The most common method was to use HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) to create documents that could be viewed in a web browser. HTML is a very basic markup language that is used to create web pages. It is not very powerful, but it is easy to learn and use. As the web grew, more people began to realize the potential of the web as a platform for sharing information. The first major breakthrough came with the invention of the web browser. The web browser allowed users to view web pages created with HTML. The web browser also allowed users to view documents created with other markup languages, such as XML (Extensible Markup Language). With the introduction of the web browser, the potential of the web as a platform for information sharing began to be realized. The next major breakthrough came with the introduction of the web server. The web server allowed users to access web pages from anywhere in the world. The introduction of the web server opened up a whole new world of possibilities for the web. The next major breakthrough came with the introduction of the web application. The web application allowed users to interact with the web server. The web application allowed users to create and edit documents, to send and receive email, and to do many other things that were not possible with the HTML markup language. The introduction of the web application marked the beginning of the modern era of the World Wide Web.
Web architecture is the set of rules, principles, and practices that define how a website or web application is structured. It encompasses everything from the way the code is organized to the way the user interface is designed. Web architecture is important because it affects everything from the way a website loads to the way it looks and feels. Good web architecture makes a website more usable, efficient, and scalable. There are many different ways to organize a website or web application. The most common are the model-view-controller (MVC) and the model-view-viewmodel (MVVM) patterns. MVC is a way of organizing code so that the data (model), the presentation of the data (view), and the logic that controls the data (controller) are all separate. This makes it easier to develop and maintain a website or web application. MVVM is similar to MVC, but it uses a separate viewmodel layer to control the data. This makes it easier to create complex user interfaces. Both MVC and MVVM are popular web architecture patterns. There are many other patterns that can be used, depending on the needs of the website or web application.
In conclusion, the article discusses the various web architecture Wikipedia services that are available. It provides an overview of the different types of services that are available and how they can be used to improve the functionality of a website.
Top services about Web architecture wikipedia

I will give you an expired domain with a wikipedia backlink
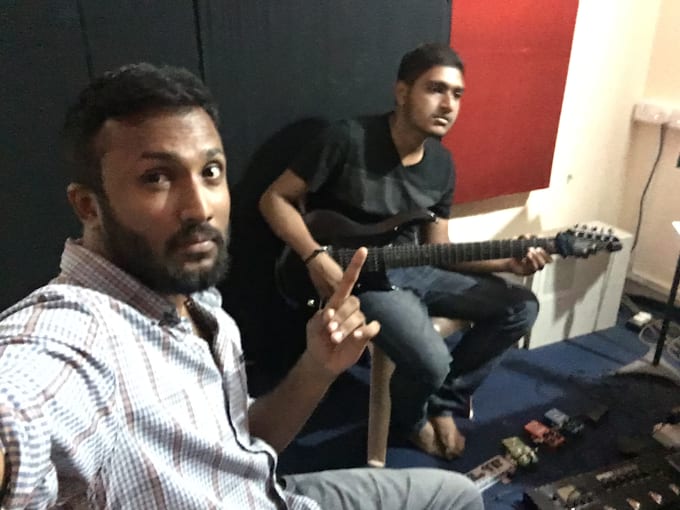

I will produce your music with production, mixing and master
to know more about me you can check my wikipedia page:- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Niranj_Suresh

I will create,live and submit an approved wilkie page for your or your business

I will translate scientific content from english to french
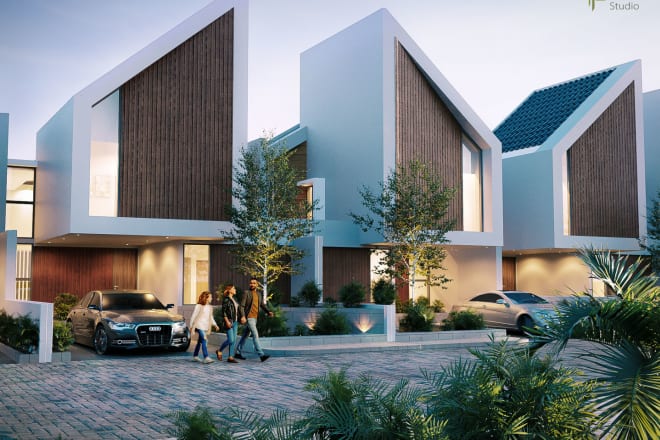

I will make 3d rendering architecture for marketing and impression

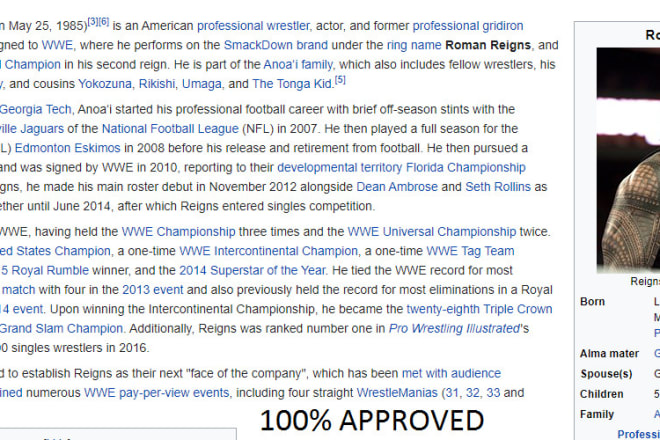
I will get your business approved on wikipedia page
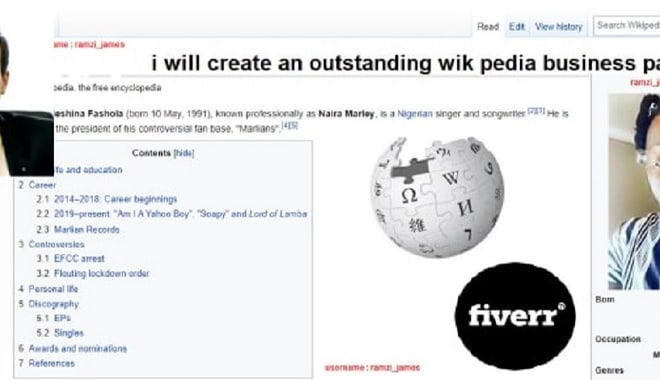
I will create an outstanding wikipedia business page

I will setup an outstanding wikipedia page for your business

I will create professionally approved wikipedia page for you and your business